What is the Anti Passback System?
The anti passback function is a security feature within access control systems designed to prevent an identification method (e.g. access card) from being used multiple times in succession to enter a secured area without first registering a proper exit. Often referred to as a "double-use lock" or "anti-replay block," this measure ensures that access credentials cannot be misused.
This means unauthorized individuals cannot gain entry to restricted areas by sharing employee badges, visitor passes, or similar identification tools. By integrating an anti passback mechanism into your company's internal access control system, you can significantly enhance the security of sensitive spaces and critical areas.
How does the anti passback system work?
The principle behind the anti passback feature is as straightforward as it is effective. Here's how the check-in and check-out process typically works:
- Entry (Check-in):
- An employee presents their access credential at the entry reader.
- The system logs the entry and updates the employee's status to "inside the area."
- Access is granted, and the door or gate opens.
- Inside the Secured Area:
- While the employee remains in the secured area, their card cannot be reused for another entry.
- Exit (Check-out):
- The employee presents their card at the exit reader.
- The system registers the exit and updates the user's status.
- The exit is unlocked.
- Re-Entry:
- The card becomes valid for entry only after a proper check-out has been completed.
By enforcing this specific sequence, companies ensure that each access credential is used exclusively by its assigned individual. This secures that unauthorized persons cannot gain access to the premises or restricted areas through credential sharing.
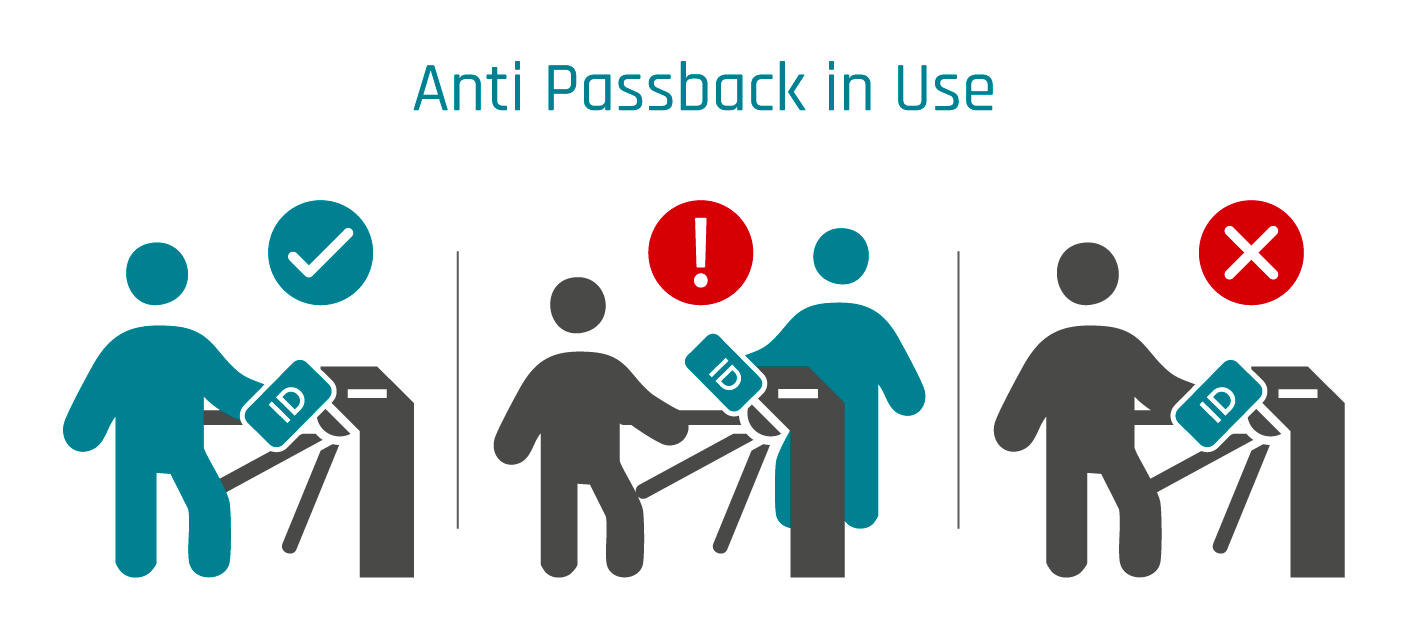
The functionality of an anti-passback system ensures controlled access to an area; Image © GFOS Group
Where Does the Anti Passback System Come in to Use?
Electronic locking systems featuring an anti passback function are now widely used across various contexts. Below are the most common applications:
- Corporate Buildings / Office Complexes:
Protect sensitive areas and manage access for visitors and employees. - Parking Garages / Underground Parking Lots:
Prevent unauthorized entry and exit of multiple vehicles using a single credential. - Stadiums / Event Venues:
Control entry and exit flow during large events and prevent ticket-sharing (often combined with anti-tailgating measures). - Industrial Facilities / Production Sites:
Secure sensitive production zones from unauthorized access and prevent accidental entry into hazardous areas. - Data Centers / Laboratories:
Protect high-security areas where preventing repeated entries and ensuring precise attendance documentation are critical.
In business environments, these anti-passback systems are typically integrated into a comprehensive access control strategy. When a credential is scanned at an access reader, the system not only checks if the person is already within the area but also verifies whether they are fundamentally authorized to access that specific zone.
Different Types of Anti Passback Systems
Depending on the use case, anti-passback mechanisms can be implemented in various forms to meet specific security needs:
Location-Based Anti Passback
This is the “classic” approach to access restriction. It prevents repeated check-ins at an entry point, such as a door, with the same credential until a valid check-out is recorded. A variation of this is global anti-passback, which ensures that a credential cannot be used simultaneously across multiple restricted areas.
Time-Based Anti Passback
This method works similarly to the classic version but introduces a time delay. After a check-out, a credential becomes valid for re-entry only after a designated period or at a specific time. This option is particularly useful in scenarios where exit activities are not routinely logged but a timed re-entry restriction is required.
Hard- / Soft-Anti-Passback
Furthermore, the double use lock can be divided into “hard” and “soft” versions. A soft version does not prevent access, but merely logs unauthorized multiple use - this can be useful for identifying whether people in the company are violating access guidelines. Hard blocks, on the other hand, ensure that access is completely denied.
Components of an Anti Passback System
For an anti passback feature to function effectively, both entry and exit readers must be installed at all access points within the controlled area. Below are the key components necessary for a seamless implementation.
Technical components
- Entry and Exit Readers: To ensure reliable operation, all access points in the secured area must have both entry and exit readers installed.
- Central Control Unit: A robust access control software paired with an access controller is essential for managing user permissions and tracking the current status of each user.
- Identification Media: Secure identification tools, such as access cards, key fobs, or biometric credentials, are required for users to interact with the reader elements at access points.
Functional Aspects
- Area Tracking: The system must accurately record and monitor each user’s current location within the controlled area. This requires pre-configuring the individual access readers and their parameters in the system.
- Alarm Management: Features for detecting, logging, and reporting anti passback violations are vital. These can include soft anti passback (logging violations without restricting access) or hard anti passback (denying access in case of violations).
Benefits of an Anti Passback System
Implementing an anti passback system at company sites offers a range of significant advantages:
- Enhanced Security: By preventing unauthorized access through the sharing of credentials, these systems substantially reduce security risks. This ensures a higher level of protection across all areas and facilities.
- Attendance Tracking: Accurate check-in and check-out logs enable detailed tracking and documentation of individual presence. Movements between multiple (secure) areas can also be monitored and visualized in real-time via a security dashboard integrated into the software.
- Preparedness for Emergencies: In case of emergencies, such as a fire, recorded credential data can be used to maintain an evacuation list. This list supports internal safety officers and emergency responders in locating individuals who may still be in the building.
- Support for Security Audits: Beyond improving overall security, the introduction of an anti passback function helps meet strict compliance requirements. This is particularly valuable during audits related to data protection (e.g., GDPR) or information security management systems (ISMS), which often demand rigorous standards.
Challenges of an Anti Passback System
However, integrating an anti passback feature into a company’s access control system comes with some notable challenges:
- Increased Complexity: Adding the mechanism raises the overall complexity of the security system, especially in terms of daily operations and system management.
- Higher Investment Costs: Implementing the system requires compatible access readers capable of supporting the anti passback feature. The more readers needed, the greater the associated costs.
- Greater Maintenance Requirements: Due to their critical role in ensuring security, these additional readers require more frequent inspection and maintenance, increasing the overall workload for the facilities team.
Combining Anti Passback System with Additional Systems
While a modern access control system with an anti passback function already provides a high level of security, additional authentication mechanisms can be implemented to meet more stringent protection requirements. The following combinations are particularly effective:
PIN Codes
Assigning unique PIN codes to individuals ensures that access is explicitly tied to a specific employee. If an access card is stolen without immediate detection, it becomes essentially useless without the associated PIN. This two-factor authentication method is highly effective in preventing unauthorized use of credentials.
Two-Person Rule
This setup requires a second person to confirm every access attempt—either by using their own access card simultaneously or by granting approval through a terminal within the secure area. This approach not only prevents employees from sharing their credentials but also allows for visual confirmation by a security officer. For example, the officer can verify that the individual seeking access matches the authorized employee’s profile.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric access control is particularly useful in environments with the highest security requirements. By integrating individual identification methods (such as a chip card) and an anti passback system with biometric data—like hand vein scanning—unauthorized or unlogged access to restricted areas becomes nearly impossible. Such solutions are commonly deployed in high-security facilities.
Enhance Your Security with GFOS.Access Control
Leverage the extensive features of modern access control solutions. Contact us today for comprehensive advice on how our innovative access control systems can help secure your organization.